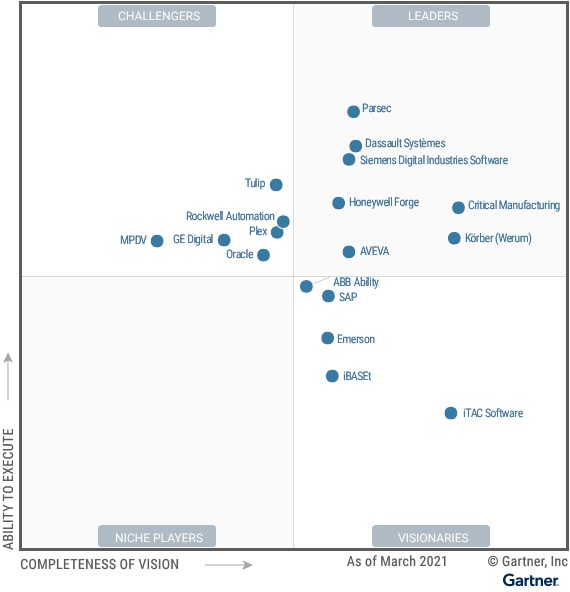
B Investors with guidance on the types of information they should expect of companies to manage portfolio risks related to physical climate change impacts. Weve spent a lot of time now looking at both the physical risk and transition risk posed by climate change.
Containing an open repeatable methodology which.
Climate change physical risk. The first is physical risk in other words the economic impact stemming from the expected increase in the frequency and magnitude of natural hazards. According to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 119 weather and climate disasters that each entailed more than US1 billion in property damage have occurred in the United States since 2010roughly twice the number of such events that occurred in the. Stress testing and climate risk disclosure are essential to better assess physical risk.
Physical risks on the other hand are likely to be unavoidable. The physical one in particular is I think underappreciated in how near term it is how nonlinear some of the impacts are. This guide should also be useful for the public and policymak-ers seeking to better understand the critical issues concerning.
Physical climate-related risks represent the financial and economic losses due to the increasing frequency and intensity of climate-related events such as floods heatwaves or hurricanes and the consequences of long-term changes in climate trends such as rising sea levels acidification of the oceans and changes in precipitation due to rapidly increasing. 4 Climate change can both amplify traditional risks and create new risks. Specifically it provides.
Physical effects of global warmingrising sea levels drier droughts stormier stormsimperil factories and other assets as well as transport and energy links that knit supply chains together. Acute physical risks refer to those that are event-driven. To physical risks seems remiss.
Seven characteristics stand out. Physical risks resulting from climate change can be event driven acute or longer-term shifts chronic in climate patterns. Physical risk transition risk and liability risk.
Climate change risk can arise through three key categories. Beyond climate change mitigation and adaptation sovereign financial strength and higher insurance penetration help to preserve financial stability. On physical climate risk disclosure and risk management steps.
Investors and lenders can follow refining to suit their. Common approaches to risk assessment and risk management strategies based on natural hazards have been applied to climate change impacts although there are. Businesses recognise the threat.
The future path of greenhouse gas emissions will depend crucially on the adoption of climate policies and technological innovations IPCC 2018. In each of our nine cases the level of physical climate risk increases by 2030 and further by 2050. Climate change as a source of systemic risk Climate-related risks to the economy and financial sector are usually divided into two categories.
A clear and present danger Extreme weather events failure of climate change adaptation and natural catastrophes were ranked in the top 10 risks for business leaders in East Asia and the Pacific and. A Publicly-traded companies with detailed and specific guidance on physical climate risk disclosure and risk management steps. Climate risks are primarily viewed through three lenses.
Physical climate risk is. Within EBRD we are operating in some of the worlds most climate-vulnerable regions and so we fully understand the importance of assessing managing and disclosing the physical climate risks. Regulation fossil fuel exposure and clean energy growth.
Examples of recent weather events that have been linked to human-driven climate change include the heatwave and droughts in China in the summer of 2013 and the following winter extreme. Physical risk relates to the impact of events related to climate changesuch as severe stormson property infrastructure and business supply chains. Physical risks of climate change.
Climate risk refers to risk assessments based on formal analysis of the consequences likelihoods and responses to the impacts of climate change and how societal constraints shape adaptation options. Climate change presents material risks to business financial markets and society as a whole and these will only increase as the impacts of climate change become more apparent. Physical risks such as rising temperatures flooding drought sea level rise and water scarcity - are already being felt globally and the associated financial losses both insured and uninsured have significantly increased in recent years.
Property damage from physical climate risk has become increasingly common. Climate change physical risk does not appear to be reflected in global equity valuations. Climate change means we may face more frequent or severe weather events like flooding droughts and storms.
We find that physical risk from a changing climate is already present and growing. Physical risks are the risks associated with the physical effects of climate change. Climate change creates physical and transition financial risk Recent climate change has been driven by increased levels of carbon dioxide CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
What are the physical risks from climate change. The physical risk framework is a practical guide. The methodology has the potential to become.
Also as we know the impacts will be systemic and potentially highly regressive. All are important but rely on action to combat climate change that is far from assured. Investors with guidance on the types of information they should expect of companies to manage portfolio risks related to physical climate change impacts.
With natural catastrophe models to assess some of the physical risks of climate change in different scenarios.